How to Bind Can Execute
Whether a control, that can initiate an action in response to user interaction, is in its enabled state, is an important principle of the 'revealed functionality' part of user experience design (UX). User confidence is reinforced by disabling commands that cannot run. For example where a button or menu item cannot run due to the current state of an application, they should be presented as inactive.
This example assumes that you are using the MVVM implementation pattern with the ReactiveUI framework. This (recommended) approach gives a very clear separation between the view and the view model.
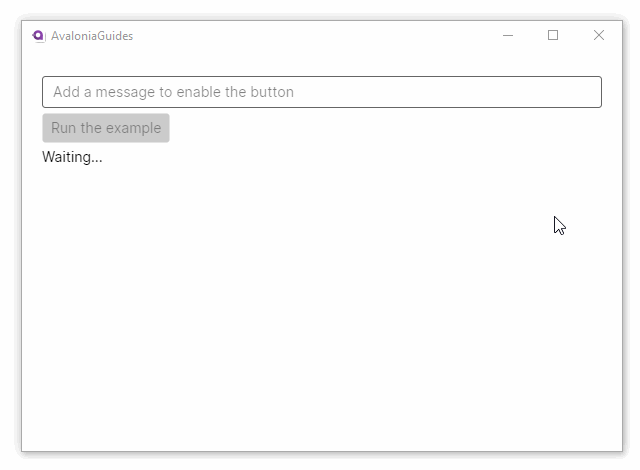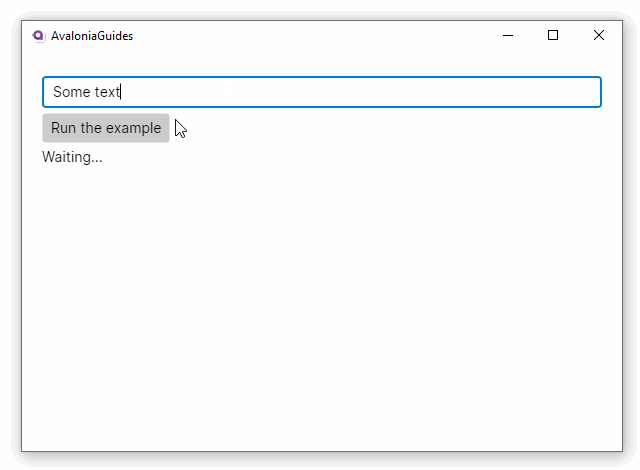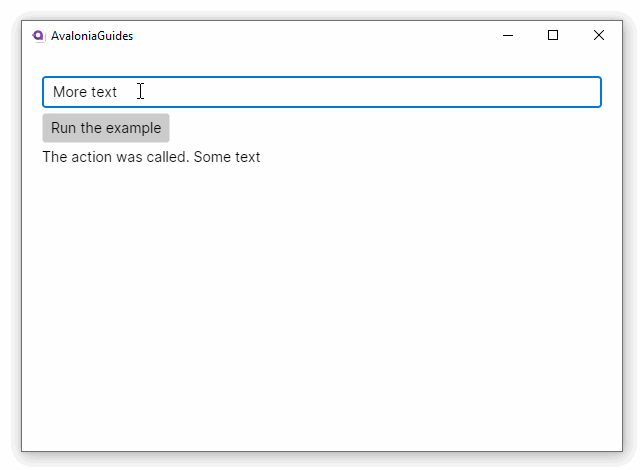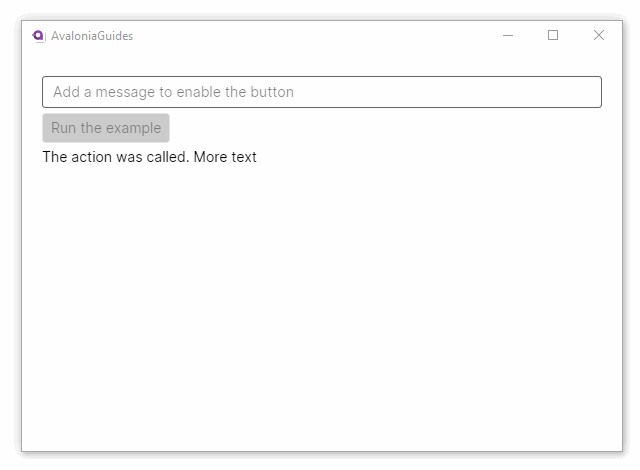
In this example, the button can only be clicked when the message is not empty. As soon as the output is shown; the message is reset to the empty string - which in turn will disable the button again.
<StackPanel Margin="20">
<TextBox Margin="0 5" Text="{Binding Message}"
Watermark="Add a message to enable the button"/>
<Button Command="{Binding ExampleCommand}">
Run the example
</Button>
<TextBlock Margin="0 5" Text="{Binding Output}" />
</StackPanel>
namespace AvaloniaGuides.ViewModels
{
public class MainWindowViewModel : ViewModelBase
{
private string _message = string.Empty;
private string _output = "Waiting...";
public string Message
{
get => _message;
set => this.RaiseAndSetIfChanged(ref _message, value);
}
public string Output
{
get => _output;
set => this.RaiseAndSetIfChanged(ref _output, value);
}
public ReactiveCommand<Unit, Unit> ExampleCommand { get; }
public MainWindowViewModel()
{
var isValidObservable = this.WhenAnyValue(
x => x.Message,
x => !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(x));
ExampleCommand = ReactiveCommand.Create(PerformAction,
isValidObservable);
}
private void PerformAction()
{
Output = $"The action was called. {_message}";
Message = String.Empty;
}
}
}
using ReactiveUI;
namespace AvaloniaGuides.ViewModels
{
public class ViewModelBase : ReactiveObject
{
}
}
In the constructor of the view model, the reactive command is created with two parameters. The first is the private method that performs the action. The second is an observable which is created by the WhenAnyValue method of the ReactiveObject that underlies the view model (from the ViewModelBase class).
The ViewModelBase class is added to your project when you use the 'Avalonia MVVM Application' solution template.
Here the WhenAnyValue method takes two arguments, the first collects a value for the parameter of the validation function, and the second is the validation function that returns a Boolean result.
The WhenAnyValue method actually has overloads that can take up to 10 different value getters (for the validation function parameters), plus the validation function itself.