What is Avalonia?
Avalonia is an open-source, cross-platform UI framework that enables developers to create application using .NET for Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, Android and WebAssembly.
It uses its own rendering engine to draw UI controls, ensuring consistent appearance and behavior across all supported platforms. This means that developers can share their UI code and maintain a uniform look and feel regardless of the target platform.
Who Avalonia is for?
Avalonia is for developers who want to:
- Write cross-platform apps in XAML and C#, from a single shared code-base.
- Share UI, layout and design across multiple platforms.
- Share code, tests, and business logic across platforms.
How does Avalonia work?
Avalonia unifies desktop, mobile, and web platforms through a unique approach that differs from traditional cross-platform frameworks. Rather than wrapping native UI controls, Avalonia implements its own cross-platform rendering engine that ensures pixel-perfect consistency across all supported platforms.
Architecture Overview
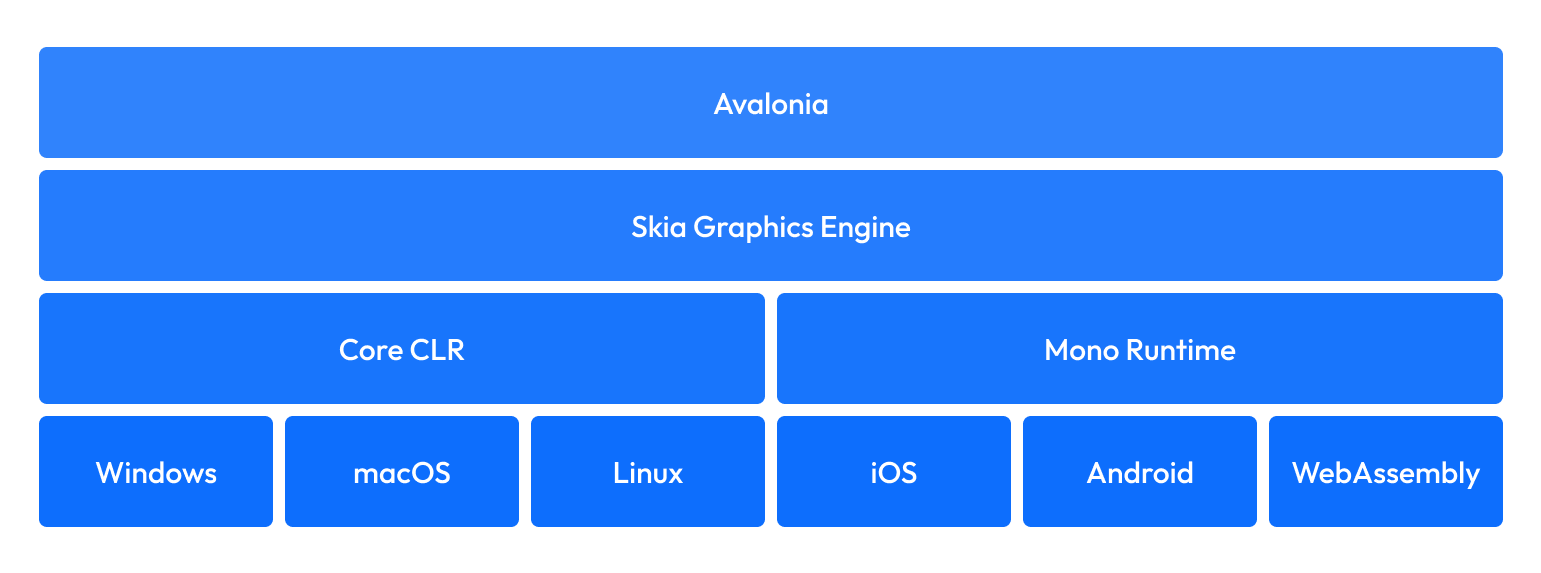
Avalonia is built on .NET Standard 2.0, allowing it to run on any platform that supports .NET. The framework consists of several key layers:
Core Platform-Agnostic Layer
The majority of Avalonia's functionality resides in a platform-agnostic core layer that handles:
- UI Controls and Layout
- Visual Tree Management
- Styling System
- Data Binding
- Input Handling
- Animation Framework
This core layer is completely platform-independent, meaning it behaves identically regardless of the operating system or device.
Rendering Engine
Unlike frameworks that rely on native UI controls, Avalonia uses its own rendering engine powered by either Skia or Direct2D. This approach means that:
- Applications look and behave identically across platforms
- Custom controls and visual effects can be implemented once and work everywhere
- The framework isn't limited by platform-specific UI capabilities
Platform Integration Layer
Avalonia requires minimal platform-specific code to integrate with each supported platform. This layer handles:
- Window Management
- Input Events
- Clipboard Operations
- Native Dialogs
- Hardware Acceleration
- Platform-Specific Features
Runtime Environment
Avalonia applications run on the .NET runtime, whether that's .NET Core, or Mono.
Comparison with Native Approaches
While frameworks like .NET MAUI abstract over native UI controls, Avalonia takes a different approach:
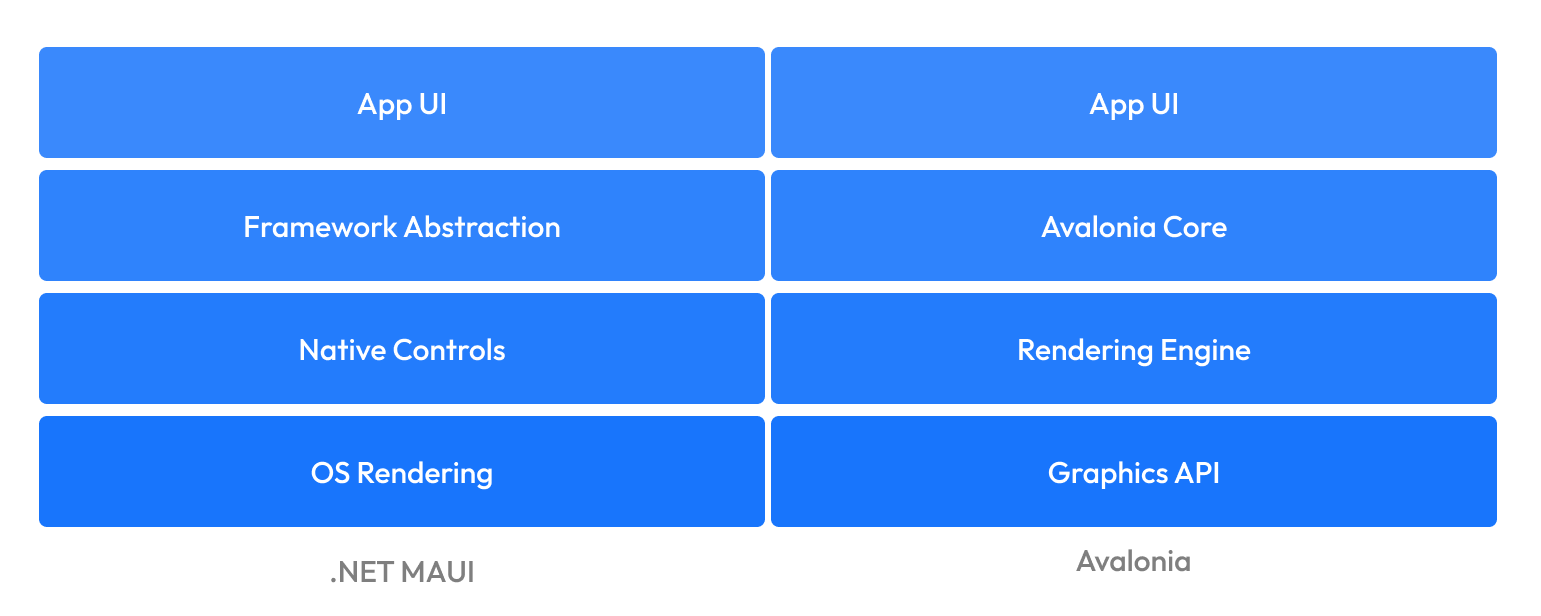
This architectural difference provides several benefits:
- Consistent behavior across platforms
- Pixel-perfect rendering
- Full control over the UI stack
- Simplified platform support
- Reduced maintenance overhead
- Better performance on resource-constrained devices
Integration with Native Platforms
While Avalonia uses its own rendering engine, it still integrates seamlessly with native platform capabilities:
- Windows: Supports Win32 APIs and modern Windows features
- Linux: Works with X11, Wayland, and framebuffer rendering
- macOS: Integrates with Cocoa and platform services
- Mobile: Provides native lifecycle management and platform integration
- Web: Runs via WebAssembly with full browser integration
Platform Support Requirements
At its core, Avalonia requires just two fundamental capabilities to support a new platform:
- The ability to draw pixels on a screen
- The ability to receive input events
This minimal requirement set is what allows Avalonia to support such a wide range of platforms, from desktop operating systems to embedded devices, and even unusual platforms like VNC servers.
This architecture enables Avalonia to deliver on its promise of "One codebase, infinite possibilities" while maintaining high performance and native platform integration where it matters most.