How To Access the UI Thread
This guide will show you how to access the UI thread in your Avalonia UI application.
Avalonia UI applications have one main thread, and this handles the UI. When you have a process that is intensive, or long running, then you will usually opt to run it on a different thread. Then you may have scenarios where you want to update them main UI thread (for example with progress updates).
A dispatcher provides services for managing work items on any specific thread. In Avalonia UI you will already have the dispatcher that handles the UI thread. When you need to update the UI from a different thread, you access it through this dispatcher, as follows:
Dispatcher.UIThread
You can use either the Post method or the InvokeAsync method to run a process on the UI thread.
Use Post when you just want to start a job, but you do not need to wait for the job to be finished, and you do not need the result: this is the 'fire-and-forget' dispatcher method.
Use InvokeAsync when you need to wait for the result, and potentially want to receive the result.
Dispatcher Priority
Both of the above methods have a dispatcher priority parameter. You can use this with the DispatcherPriority enumeration to specify the queue priority that the given job should be given.
For the possible values of the DispatcherPriority enumeration, see here.
Example
In this example a text block is used to show the result of a long running task, and a button is used to start the work. In this version, the fire-and-forget Post method is used:
<StackPanel Margin="20">
<Button x:Name="RunButton" Content="Run long running process"
Click="ButtonClickHandler" />
<TextBlock x:Name="ResultText" Margin="10"/>
</StackPanel>
using System.Threading.Tasks;
...
private async Task LongRunningTask()
{
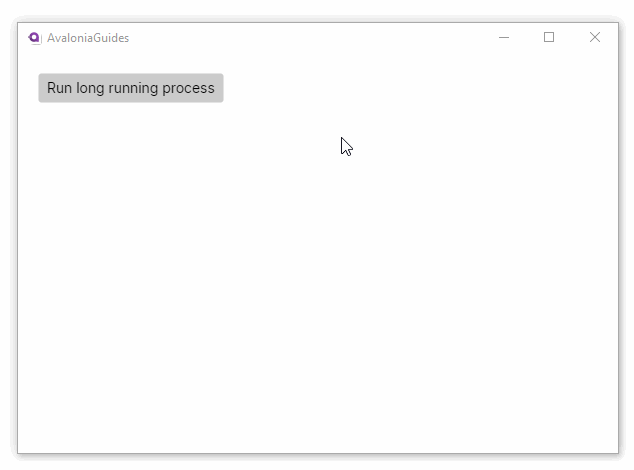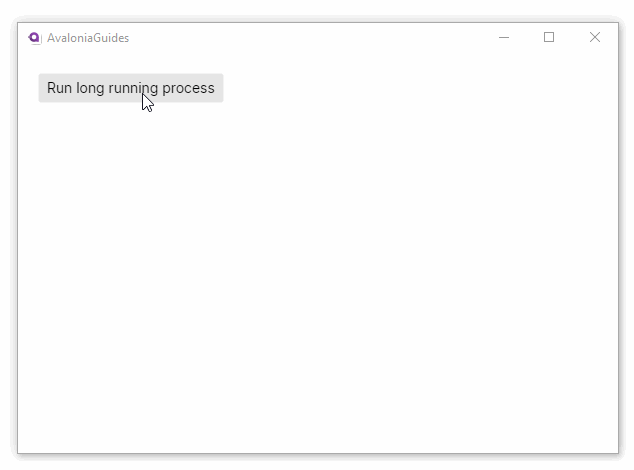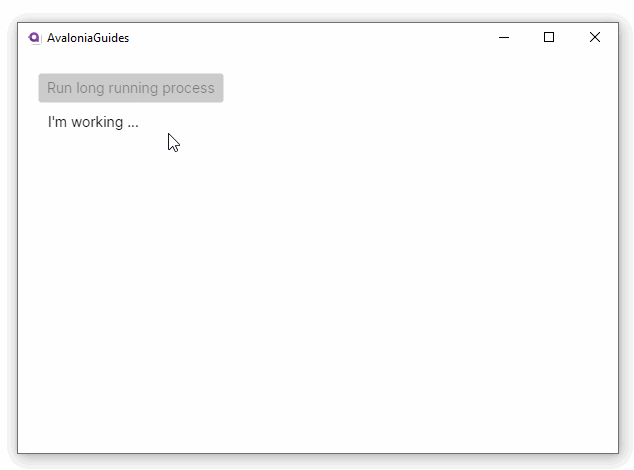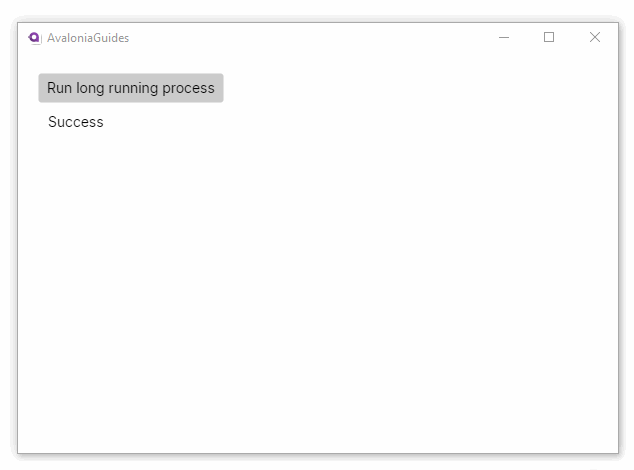
this.FindControl<Button>("RunButton").IsEnabled = false;
this.FindControl<TextBlock>("ResultText").Text = "I'm working ...";
await Task.Delay(5000);
this.FindControl<TextBlock>("ResultText").Text = "Done";
this.FindControl<Button>("RunButton").IsEnabled = true;
}
private void ButtonClickHandler(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// Start the job and return immediately
Dispatcher.UIThread.Post(() => LongRunningTask(),
DispatcherPriority.Background);
}
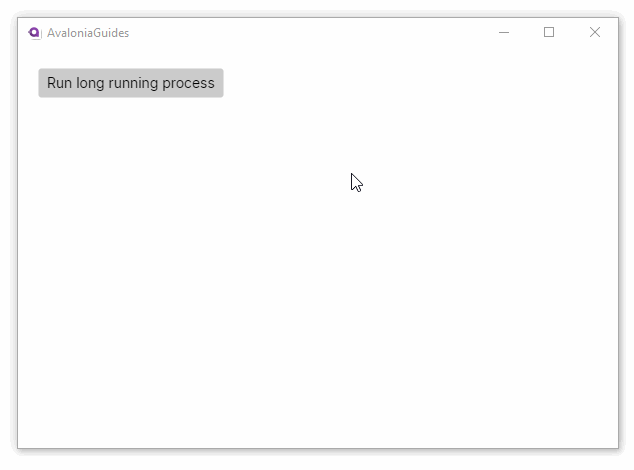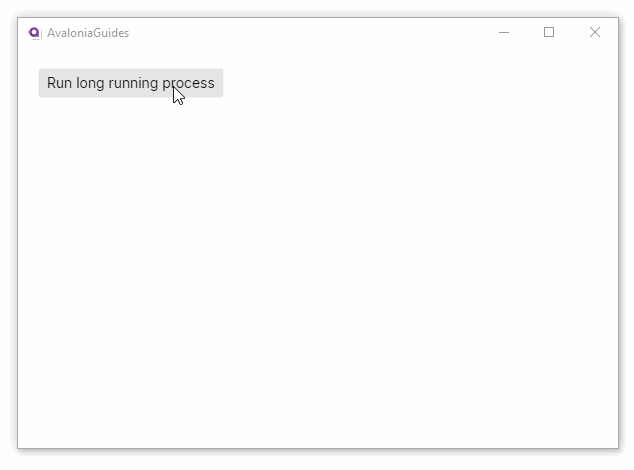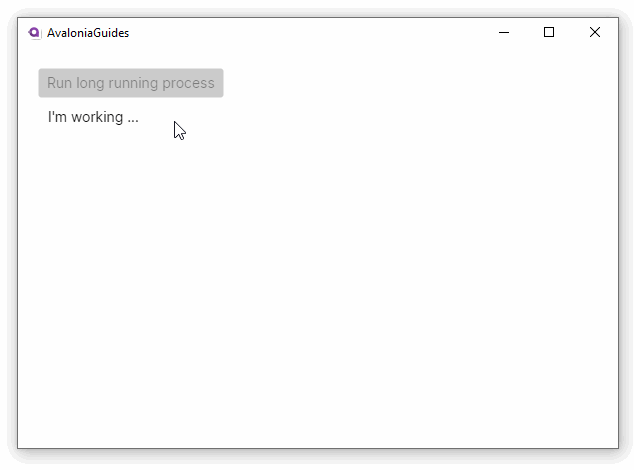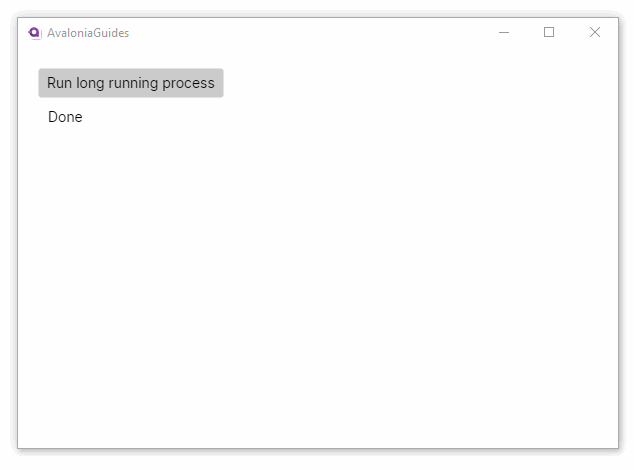
Notice that because the long running task is executed on its own thread, the UI does not lose responsiveness.
To get a result from the long running task, the XAML is the same, but this version uses the InvokeAsyncmethod:
<StackPanel Margin="20">
<Button x:Name="RunButton" Content="Run long running process"
Click="ButtonClickHandler" />
<TextBlock x:Name="ResultText" Margin="10" />
using System.Threading.Tasks;
...
private async Task<string> LongRunningTask()
{
this.FindControl<Button>("RunButton").IsEnabled = false;
this.FindControl<TextBlock>("ResultText").Text = "I'm working ...";
await Task.Delay(5000);
return "Success";
}
private async void ButtonClickHandler(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
var result = await Dispatcher.UIThread.InvokeAsync(LongRunningTask,
DispatcherPriority.Background);
//result returns here
this.FindControl<TextBlock>("ResultText").Text = result;
this.FindControl<Button>("RunButton").IsEnabled = true;
}
More Information
For the complete API documentation about the dispatcher, see here.
View the source code on GitHub Dispatcher.cs